Introduction
Understanding how to check if your suspension is good empowers vehicle owners to identify potential problems early, prevent costly repairs, and maintain optimal driving safety. Modern suspension systems represent complex assemblies of interconnected components working together to provide ride comfort, handling stability, and tire contact maintenance across diverse driving conditions.
Checking suspension condition requires systematic evaluation of multiple components including shock absorbers, struts, springs, bushings, and mounting hardware through visual inspection, performance testing, and driving assessment procedures. Good suspension system indicators include consistent ride quality, stable handling characteristics, even tire wear patterns, absence of unusual noises, and proper vehicle stance without sagging or leaning tendencies.
The importance of regular suspension condition assessment extends beyond comfort considerations to encompass critical safety factors including braking effectiveness, steering response, and stability control system operation. This comprehensive guide provides detailed instructions for checking suspension system health through proven diagnostic methods accessible to vehicle owners with basic mechanical knowledge.
Visual Inspection Methods for Suspension Assessment
External Component Examination
Visual suspension inspection represents the foundation of effective suspension condition checking, providing immediate identification of obvious problems and component damage:
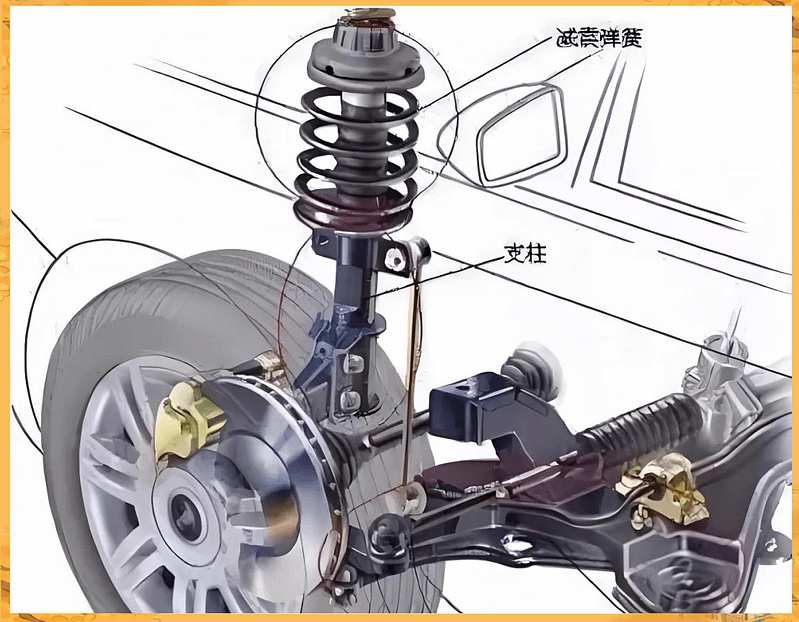
Shock Absorber Assessment: Examine shock absorber bodies for signs of fluid leakage, which appears as wet or oily surfaces around the shock body, mounting points, or ground beneath the vehicle. Leaking shock absorbers indicate internal seal failure requiring immediate replacement to maintain proper damping function.
Spring Condition Evaluation: Inspect coil springs for visible damage indicators including cracks, breaks, or sagging that affects vehicle height and handling characteristics. Broken suspension springs create immediate safety hazards and require emergency professional attention to prevent loss of vehicle control.
Bushing Deterioration Signs: Examine rubber bushings throughout the suspension system for cracking, separation, or missing material that allows excessive component movement. Worn suspension bushings create handling problems, noise issues, and accelerated wear of adjacent components.
Mounting Hardware Inspection: Check all suspension mounting bolts, brackets, and hardware for proper torque, corrosion damage, or wear indicators suggesting structural integrity concerns requiring professional evaluation and potential replacement.
Tire Wear Pattern Analysis
Tire wear inspection provides detailed information about suspension system condition and alignment status through systematic examination of wear patterns:
Even Wear Indicators: Good suspension systems produce uniform tire wear across the entire tread surface, indicating proper alignment, adequate shock absorber function, and correct suspension geometry throughout the contact patch.
Inside Edge Wear: Excessive wear on tire inner edges typically indicates suspension alignment problems including worn ball joints, control arm bushing failure, or damaged strut mounts affecting camber angles during vehicle operation and requiring professional correction.
Outside Edge Wear: Outer tire edge deterioration suggests suspension geometry issues including insufficient camber correction, worn suspension components allowing excessive wheel movement, or improper alignment following suspension service work.
Cupping or Scalloping: Irregular wear patterns creating high and low spots around tire circumference indicate shock absorber problems or worn suspension components allowing wheel oscillation rather than controlled damping movement.
Performance Testing Procedures
Bounce Test Method
The suspension bounce test provides immediate feedback about shock absorber and strut condition through systematic evaluation of damping effectiveness:
Test Procedure Execution: Position yourself at each corner of the vehicle and push down firmly on the body above each wheel, creating suspension compression. Release quickly and observe suspension response characteristics including rebound speed, oscillation frequency, and settling behavior.
Good Suspension Response: Properly functioning suspension systems should exhibit controlled rebound motion with the vehicle returning to normal height within one full cycle without excessive bouncing, oscillation, or delayed settling indicating adequate damping function.
Failed Component Indicators: Worn shock absorbers or struts allow excessive bouncing motion where the vehicle continues oscillating after the initial compression release, indicating insufficient damping capability requiring component replacement.
Corner-to-Corner Comparison: Perform the bounce test systematically at each vehicle corner, comparing responses to identify individual component problems or inconsistent damping characteristics between left and right sides suggesting uneven wear patterns.
Road Testing Assessment
Dynamic suspension testing through controlled driving evaluation provides comprehensive performance assessment under realistic operating conditions:
Handling Characteristics: Drive the vehicle through gentle cornering maneuvers while monitoring body roll, steering response, and stability indicators. Good suspension systems provide controlled body movement without excessive lean, wandering, or instability during direction changes.
Braking Performance: Test suspension response during braking by applying moderate brake pressure while observing nose dive behavior, vehicle stability, and stopping characteristics. Proper suspension function maintains vehicle control without excessive forward pitch or directional instability.
Bump and Pothole Response: Drive over speed bumps, railroad crossings, and minor road irregularities while assessing impact absorption, rebound control, and passenger comfort. Effective suspension systems absorb impacts smoothly without harsh jolts, excessive bouncing, or noise transmission.
Noise and Vibration Evaluation
Suspension-related sounds provide diagnostic information about component condition and wear status:
Clunking Sounds: Listen for impact-type noises during suspension movement over bumps or during direction changes. Suspension clunking sounds typically indicate loose components, worn bushings, or internal shock absorber damage requiring professional diagnosis and repair.
Squeaking Noises: High-pitched sounds during suspension operation often suggest bushing wear, lubrication problems, or component friction requiring attention to prevent accelerated wear and component failure.
Grinding Sounds: Harsh, abrasive noises indicate severe suspension wear suggesting metal-to-metal contact and requiring immediate professional evaluation to prevent safety hazards and expensive component damage.
Measuring and Assessment Techniques
Vehicle Height Measurement
Suspension sag assessment through systematic height measurement reveals spring condition and load-carrying capacity:
Measurement Procedure: Use a tape measure or ruler to measure distance from wheel center to fender edge at each corner, comparing measurements between left and right sides to identify suspension sagging or uneven height indicating spring weakness or failure.
Normal Height Specifications: Consult vehicle manufacturer specifications for proper ride height measurements, typically ranging within 1/2 inch tolerance between sides for acceptable suspension condition and proper load distribution.
Load Testing: Measure vehicle height with and without typical cargo loads to assess spring rate adequacy and suspension response under normal operating conditions. Excessive height reduction under load suggests spring weakness or shock absorber problems.
Weight Distribution Analysis
Vehicle stance evaluation provides information about overall suspension system balance:
Front-to-Rear Assessment: Compare front and rear vehicle height according to manufacturer specifications, identifying suspension problems affecting vehicle attitude including spring sag, shock absorber failure, or load distribution issues.
Side-to-Side Comparison: Measure and compare left and right side heights at both front and rear positions to identify individual component problems or uneven wear patterns affecting vehicle balance and handling characteristics.
Warning Signs Requiring Professional Attention
Critical Safety Indicators
Immediate professional evaluation becomes necessary when encountering serious suspension warning signs:
Handling Instability: Any sudden changes in vehicle control, steering response, or directional stability represent critical suspension safety issues requiring immediate professional diagnosis to prevent dangerous driving situations and potential accidents.
Structural Component Damage: Visible damage to suspension components including bent parts, broken springs, or separated connections indicates immediate suspension problems requiring emergency professional attention and component replacement.
Multiple Simultaneous Symptoms: Several suspension problem indicators occurring together suggest systematic component failure requiring comprehensive professional diagnosis and coordinated repair procedures.
Progressive Wear Indicators
Developing suspension problems exhibit characteristic warning sign patterns:
Gradual Performance Degradation: Progressive changes in ride quality, handling characteristics, or noise levels suggest normal component wear requiring scheduled professional evaluation and maintenance planning.
Increasing Tire Wear: Accelerating tire wear patterns or changing wear characteristics indicate developing suspension problems requiring professional diagnosis and correction to prevent expensive tire replacement costs.
Comfort Reduction: Decreasing ride comfort including increased harshness, motion, or impact transmission suggests shock absorber wear or spring degradation requiring professional assessment and component replacement.
Executive Summary (500 words)
Understanding how to check if your suspension is good empowers vehicle owners to maintain safety, identify potential problems early, and make informed maintenance decisions. Effective suspension condition assessment requires systematic evaluation combining visual inspection, performance testing, and driving evaluation procedures accessible to owners with basic mechanical knowledge.
Visual suspension inspection forms the foundation of condition assessment through examination of shock absorbers for fluid leakage, springs for damage or sagging, bushings for deterioration, and mounting hardware for wear or damage. Tire wear pattern analysis provides detailed information about suspension alignment and component condition, with even wear indicating good suspension function while irregular patterns suggest specific component problems requiring attention.
Performance testing procedures including the bounce test method offer immediate feedback about shock absorber and strut effectiveness through controlled compression and release cycles. Good suspension systems exhibit controlled rebound with minimal oscillation, while worn components allow excessive bouncing indicating replacement needs. Road testing assessment through systematic driving evaluation reveals suspension performance under realistic conditions including handling, braking, impact absorption, and stability characteristics.
Measuring and assessment techniques provide quantitative evaluation through vehicle height measurement revealing spring condition and load-carrying capacity. Weight distribution analysis identifies suspension system balance and individual component problems affecting vehicle stance and handling characteristics. Systematic measurement procedures enable objective condition assessment beyond subjective performance evaluation.
Warning signs requiring professional attention include critical safety indicators such as handling instability, structural component damage, or multiple simultaneous symptoms suggesting systematic failure. Progressive wear indicators including gradual performance degradation, increasing tire wear, and comfort reduction suggest developing problems requiring scheduled professional evaluation and maintenance planning.
Noise and vibration evaluation provides diagnostic information about component condition through identification of suspension-related sounds including clunking, squeaking, grinding, and rattling noises indicating specific component problems. Understanding sound characteristics enables early problem identification and appropriate service scheduling preventing component cascade failures.
Regular inspection intervals incorporating monthly visual checks, seasonal comprehensive evaluations, and mileage-based professional service ensure continued suspension system effectiveness throughout vehicle ownership. Systematic checking schedules enable early problem detection while preventing expensive component failures and safety hazards.
Professional diagnostic advantages including specialized equipment access, technical expertise, and warranty protection provide superior evaluation capabilities beyond consumer inspection methods. Expert assessment ensures accurate problem identification, comprehensive safety evaluation, and appropriate repair recommendations maintaining vehicle safety and performance standards.
Effective suspension checking combines multiple evaluation methods providing comprehensive condition assessment through visual inspection, performance testing, measurement procedures, and professional consultation. Understanding these inspection techniques enables confident suspension system evaluation while making informed maintenance decisions protecting vehicle safety, performance, and long-term reliability throughout ownership.
Proactive suspension maintenance through regular condition checking prevents expensive repairs, maintains vehicle safety, and ensures optimal driving experience while protecting passenger welfare and vehicle investment value.