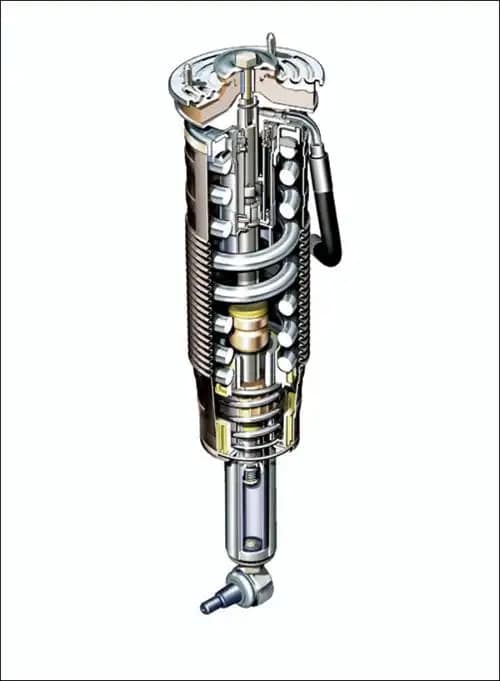
Introduction
As a leading shock absorber manufacturing facility with over thirty years of precision engineering expertise and comprehensive quality control operations, we analyze thousands of defective shock absorber units annually to understand failure patterns and acoustic signatures. Our extensive field testing data and manufacturing experience provide authoritative insights into the specific sounds that vehicles produce when shock absorbers deteriorate or fail completely.
Understanding the distinctive sounds of bad shocks enables vehicle owners, automotive technicians, and maintenance professionals to identify shock absorber problems before they compromise vehicle safety or cause expensive secondary damage. Through our rigorous manufacturing testing protocols and comprehensive failure analysis programs, we’ve documented the characteristic noise patterns that consistently indicate shock absorber deterioration requiring professional attention.
Modern shock absorbers incorporate sophisticated hydraulic systems, precision valving, and advanced sealing technology designed to operate silently throughout their service life. When these critical components begin failing, they produce unmistakable acoustic signatures that experienced professionals can interpret to determine failure severity and appropriate repair strategies.
Primary Sound Categories from Bad Shocks
Hydraulic System Failure Sounds
Bad shock absorbers experiencing internal hydraulic system failure produce distinctive fluid-related noises that indicate complete dampening loss and immediate replacement requirements for safe vehicle operation.
Fluid Sloshing and Gurgling Worn shock absorbers with internal seal failure create characteristic sloshing or gurgling sounds as hydraulic fluid moves freely within damaged chambers. This noise becomes particularly noticeable during suspension compression and extension cycles when fluid should be controlled through precision valving systems.
Our manufacturing quality control includes comprehensive hydraulic integrity testing preventing internal seal failure during normal service life. When field units develop sloshing sounds, they indicate complete hydraulic system compromise requiring immediate shock absorber replacement to restore proper dampening characteristics and vehicle control.
The sloshing sound intensifies during parking maneuvers, speed bump traversal, or road irregularity encounters as damaged seals allow unrestricted fluid movement. Professional technicians can identify this failure mode through careful listening during controlled suspension articulation testing.
Hydraulic Cavitation Noise Severely worn shock absorbers experiencing hydraulic cavitation produce distinctive bubbling or foaming sounds as air enters the hydraulic system through failed seals or damaged valving. This acoustic signature indicates advanced deterioration requiring emergency replacement to prevent suspension system failure.
Cavitation noise typically occurs during rapid suspension movement when damaged hydraulic systems cannot maintain proper fluid pressure. Our engineering analysis shows this failure mode creates complete dampening loss, allowing excessive suspension oscillation and potential vehicle control problems.
Pressure Relief Valve Noise Shock absorbers with damaged pressure relief systems create whistling or hissing sounds during compression cycles as hydraulic pressure escapes through compromised valving. This noise indicates internal component failure and immediate replacement requirements for restored performance.
Mechanical Component Failure Sounds
Mechanical component deterioration within shock absorber assemblies produces distinctive metallic noises indicating structural damage requiring immediate professional attention to prevent safety hazards.
Piston Rod Binding and Scoring Damaged shock absorber piston rods experiencing binding or scoring create harsh grinding or scraping sounds during suspension travel. This noise indicates severe internal wear affecting proper piston movement and hydraulic system function.
Piston rod binding typically results from contamination, inadequate lubrication, or manufacturing defects allowing dirt ingress into precision-machined surfaces. Our quality control protocols include comprehensive rod surface inspection and protective coating application preventing premature wear.
The grinding sound intensifies during suspension compression when damaged rods contact cylinder walls or internal components. Professional diagnosis requires immediate attention as this failure mode can cause complete shock absorber seizure and potential suspension system damage.
Internal Spring and Guide Wear Worn internal springs, guides, or positioning components create rattling or clicking sounds during shock absorber operation. These noises indicate component deterioration affecting proper internal alignment and hydraulic flow control.
Our manufacturing assembly procedures include precise component positioning and tolerance verification preventing internal wear during normal operation. Field failures producing rattling sounds typically indicate extreme operating conditions or component age exceeding design specifications.
Mounting Hardware Deterioration Shock absorber mounting hardware experiencing wear or damage creates characteristic metallic clunking or banging sounds during suspension articulation. These noises indicate loose connections requiring immediate tightening or component replacement for safe operation.
Mounting hardware failure allows excessive shock absorber movement during suspension travel, creating impact sounds as components contact mounting surfaces or adjacent parts. Our installation specifications define proper torque requirements preventing hardware loosening during service.
Environmental and Temperature-Related Sounds
Cold Weather Operation Noise Shock absorbers experiencing seal hardening or hydraulic fluid thickening during cold weather create temporary squeaking or groaning sounds until operating temperature stabilizes. While often temporary, persistent cold-weather noise may indicate developing seal problems requiring professional evaluation.
Our manufacturing specifications include cold-weather testing ensuring proper operation across expected temperature ranges. Persistent noise during cold operation suggests seal deterioration or inappropriate fluid specifications requiring replacement with premium components.
High-Temperature Degradation Sounds Overheated shock absorbers experiencing thermal degradation create hissing or steaming sounds as seals fail and hydraulic fluid deteriorates. This noise indicates severe operating conditions exceeding design parameters and immediate replacement requirements.
High-temperature operation typically results from excessive loading, inadequate cooling, or severe duty cycles beyond normal design specifications. Our thermal testing protocols validate performance under extreme conditions, though field operation may exceed these parameters.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
Professional Sound Analysis Methods
Accurate diagnosis of shock absorber sounds requires systematic analysis techniques differentiating between various failure modes and determining appropriate repair strategies for optimal outcomes.
Electronic Stethoscope Testing Professional automotive stethoscopes enable precise sound source isolation by eliminating ambient noise and focusing on specific component acoustic signatures. This diagnostic tool helps technicians differentiate between shock absorber noise and other suspension component sounds.
Our manufacturing facility uses advanced acoustic measurement equipment for quality control testing, establishing reference standards for normal operating sounds versus failure indicators. Professional technicians employ similar equipment for accurate field diagnosis.
Road Test Sound Correlation Systematic road testing under controlled conditions enables correlation between specific driving scenarios and shock absorber noise production. This diagnostic approach identifies triggering conditions and failure severity for appropriate repair planning.
Professional road test procedures include various speed ranges, road surface types, and loading conditions isolating noise sources and determining failure progression. Our field testing protocols establish baseline performance standards for comparison during diagnostic procedures.
Load and Environmental Analysis
Vehicle Loading Effects Vehicle loading significantly affects shock absorber operation and associated noise production. Empty vehicle testing may mask some failure sounds while loaded conditions intensify others, requiring comprehensive evaluation under various loading scenarios.
Load-based testing helps isolate failure modes to specific shock absorber units and determines failure severity under normal operating conditions. Our quality control testing includes loaded condition evaluation ensuring proper performance across expected service scenarios.
Temperature Documentation Shock absorber noise characteristics often change with ambient temperature, providing diagnostic clues regarding failure modes and component condition. Cold weather may intensify some sounds while hot conditions affect others differently.
Manufacturing Quality Prevention
Production Quality Control Standards
Our manufacturing facility implements rigorous quality control standards preventing noise-producing defects through comprehensive testing, material verification, and assembly procedures ensuring silent operation throughout design service life.
Hydraulic System Integrity Testing Every shock absorber undergoes extensive hydraulic testing including pressure verification, seal integrity confirmation, and flow rate measurement ensuring proper dampening characteristics without noise production. These protocols prevent field failures and associated acoustic problems.
Hydraulic testing includes both static pressure evaluation and dynamic cycling under simulated road conditions. Components failing performance standards receive immediate corrective action or rejection preventing noise-producing units from reaching customers.
Mechanical Component Verification Precision measurement and inspection of all mechanical components including piston rods, cylinders, valving, and internal hardware ensures proper fit, finish, and function preventing noise-producing wear or binding during operation.
Component verification includes surface finish measurement, dimensional tolerance confirmation, and material hardness testing ensuring optimal performance and silent operation. Advanced manufacturing techniques eliminate potential noise sources during production.
Advanced Materials and Design
Premium Seal Technology Our manufacturing utilizes advanced seal materials and designs providing superior performance, longevity, and silent operation compared to conventional alternatives. Premium seals prevent hydraulic leakage and associated noise production throughout extended service life.
Seal technology includes multiple sealing stages, advanced materials, and precision manufacturing ensuring leak-proof operation under extreme conditions. Investment in premium seal systems prevents field failures and associated noise problems.
Precision Valving Systems Advanced valving technology provides optimal hydraulic control while maintaining silent operation throughout the service life. Precision manufacturing ensures consistent performance without noise-producing flow restrictions or cavitation.
Professional Repair and Replacement
Diagnostic Confirmation Procedures
Professional shock absorber diagnosis requires systematic testing including visual inspection, manual function testing, and road evaluation confirming failure modes and determining appropriate repair strategies.
Diagnostic protocols include bounce testing, leak inspection, mounting hardware evaluation, and comparative testing between vehicle sides. This systematic approach ensures accurate problem identification and effective repair solutions.
Replacement Component Selection
Proper repair requires premium replacement shock absorbers meeting or exceeding original equipment specifications ensuring restored performance, silent operation, and extended service life compared to inferior alternatives.
Our manufacturing standards exceed OEM requirements providing superior performance, durability, and acoustic characteristics. Quality replacement components ensure effective repair and prevent recurring noise problems.
Maintenance and Prevention Strategies
Regular Inspection Guidelines
Regular visual inspection enables early detection of shock absorber deterioration including seal leakage, mounting hardware wear, and protective boot damage before noise-producing failures develop.
Visual inspection should include leak detection, mounting hardware evaluation, and protective component assessment every 25,000 miles or according to manufacturer recommendations. Early detection prevents major failures and associated repair costs.
Preventive Service Recommendations
Following manufacturer-recommended service intervals significantly reduces shock absorber failure and associated noise production through early problem identification and preventive replacement before component deterioration.
Our recommended replacement intervals consider operating conditions, vehicle usage patterns, and environmental factors ensuring optimal performance throughout vehicle service life while preventing noise-producing failures.
Conclusion
Through our extensive manufacturing experience and comprehensive failure analysis programs, we’ve identified that bad shock absorbers produce distinctive sounds including hydraulic sloshing and gurgling indicating internal seal failure; grinding and scraping from mechanical component wear; and clunking from mounting hardware deterioration. These acoustic signatures provide reliable diagnostic indicators enabling early problem identification and appropriate repair strategies.
Understanding shock absorber sounds enables proactive maintenance preventing safety hazards and expensive secondary damage. Professional diagnosis using systematic testing approaches ensures accurate failure identification and effective repair solutions using quality replacement components meeting original equipment specifications.
Our commitment to manufacturing excellence includes comprehensive acoustic testing and premium materials preventing noise-producing defects while ensuring long-term silent operation. Regular preventive maintenance and professional installation significantly reduce noise problems while maximizing shock absorber service life and vehicle safety.
As shock absorber manufacturing experts, we emphasize immediate professional attention when abnormal sounds develop, as they typically indicate component failures requiring prompt replacement for optimal vehicle safety, performance, and silent operation throughout extended service life.